Thermodynamic Database
Components (22)
Total of 22 components are included in the database as listed here:
Major alloying elements: Al, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hf, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Si, Ta, Ti, V, W, Y, and Zr
Minor alloying element: B, C, H, N and O
Suggested Composition Range
The suggested composition range for each element is listed in Table 1. The suggested composition range is estimated based on the assess subsystems as given in Section Assessed Subsystems and the validation in multi-component range as illustrated in Section Database Validation and Application.
| Elements | Composition Range (wt.%) |
|---|---|
|
Hf, Mo, Nb, Ta, V, W, Y, Zr |
0 ~ 100 |
|
Al, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Si, Ti |
0 ~ 50 |
|
B, C, H, N, O |
0 ~ 10 |
Phases
Total of 509 phases are included in the current database. The names and thermodynamic models of some phases are given in Table 2. Information on all the other phases is listed in PanRHEA2024: List of Phases. Users can also view it through TDB viewer of Pandat™.
Assessed Subsystems
A total of 423 subsystems, including 219 binary and 204 ternary subsystems have been assessed. The modeling status is indicated by numbers. The systems with number 10 are fully assessed in the whole composition range. The higher value shows higher reliability of the system.
Binary Systems (219)
| Al-B(10) | Al-C(10) | Al-Co(10) | Al-Cr(10) | Al-Cu(10) | Al-Fe(10) | Al-H(10) |
| Al-Hf(10) | Al-Mn(10) | Al-Mo(10) | Al-N(10) | Al-Nb(10) | Al-Ni(10) | Al-O(10) |
| Al-Si(10) | Al-Ta(10) | Al-Ti(10) | Al-V(10) | Al-W(10) | Al-Y(10) | Al-Zr(10) |
| B-C(10) | B-Co(10) | B-Cr(10) | B-Cu(10) | B-Fe(10) | B-Hf(10) | B-Mn(10) |
| B-Mo(10) | B-N(10) | B-Nb(10) | B-Ni(10) | B-O(10) | B-Si(10) | B-Ta(10) |
| B-Ti(10) | B-V(10) | B-W(10) | B-Y(10) | B-Zr(10) | C-Co(10) | C-Cr(10) |
| C-Fe(10) | C-Hf(10) | C-Mn(10) | C-Mo(10) | C-Nb(10) | C-Ni(10) | C-Si(10) |
| C-Ta(10) | C-Ti(10) | C-V(10) | C-W(10) | C-Y(10) | C-Zr(10) | Co-Cr(10) |
| Co-Cu(10) | Co-Fe(10) | Co-H(10) | Co-Hf(10) | Co-Mn(10) | Co-Mo(10) | Co-N(10) |
| Co-Nb(10) | Co-Ni(10) | Co-O(10) | Co-Si(10) | Co-Ta(10) | Co-Ti(10) | Co-V(10) |
| Co-W(10) | Co-Y(10) | Co-Zr(10) | Cr-Cu(10) | Cr-Fe(10) | Cr-H(10) | Cr-Hf(10) |
| Cr-Mn(10) | Cr-Mo(10) | Cr-N(10) | Cr-Nb(10) | Cr-Ni(10) | Cr-O(10) | Cr-Si(10) |
| Cr-Ta(10) | Cr-Ti(10) | Cr-V(10) | Cr-W(10) | Cr-Y(10) | Cr-Zr(10) | Cu-Fe(10) |
| Cu-H(10) | Cu-Hf(10) | Cu-Mn(10) | Cu-Mo(10) | Cu-Nb(10) | Cu-Ni(10) | Cu-O(10) |
| Cu-Si(10) | Cu-Ta(10) | Cu-Ti(10) | Cu-V(10) | Cu-W(10) | Cu-Y(10) | Cu-Zr(10) |
| Fe-H(10) | Fe-Hf(10) | Fe-Mn(10) | Fe-Mo(10) | Fe-N(10) | Fe-Nb(10) | Fe-Ni(10) |
| Fe-O(10) | Fe-Si(10) | Fe-Ta(10) | Fe-Ti(10) | Fe-V(10) | Fe-W(10) | Fe-Y(10) |
| Fe-Zr(10) | H-Hf(5) | H-Mn(10) | H-Mo(10) | H-Nb(5) | H-Ni(10) | H-Si(10) |
| H-Ta(5) | H-Ti(10) | H-V(8) | H-Zr(10) | Hf-Mn(10) | Hf-Mo(10) | Hf-N(10) |
| Hf-Nb(10) | Hf-Ni(10) | Hf-O(10) | Hf-Si(10) | Hf-Ta(10) | Hf-Ti(10) | Hf-V(10) |
| Hf-W(10) | Hf-Y(10) | Hf-Zr(10) | Mn-Mo(10) | Mn-N(10) | Mn-Nb(10) | Mn-Ni(10) |
| Mn-O(10) | Mn-Si(10) | Mn-Ta(10) | Mn-Ti(10) | Mn-V(10) | Mn-W(8) | Mn-Y(10) |
| Mn-Zr(10) | Mo-N(10) | Mo-Nb(10) | Mo-Ni(10) | Mo-O(10) | Mo-Si(10) | Mo-Ta(10) |
| Mo-Ti(10) | Mo-V(10) | Mo-W(10) | Mo-Y(10) | Mo-Zr(10) | N-Nb(10) | N-Ni(8) |
| N-Si(10) | N-Ta(10) | N-Ti(10) | N-V(10) | N-W(10) | N-Zr(10) | Nb-Ni(10) |
| Nb-O(10) | Nb-Si(10) | Nb-Ta(10) | Nb-Ti(10) | Nb-V(10) | Nb-W(10) | Nb-Y(10) |
| Nb-Zr(10) | Ni-O(10) | Ni-Si(10) | Ni-Ta(10) | Ni-Ti(10) | Ni-V(10) | Ni-W(10) |
| Ni-Y(10) | Ni-Zr(10) | O-Si(10) | O-Ta(10) | O-Ti(10) | O-V(10) | O-W(10) |
| O-Y(10) | O-Zr(10) | Si-Ta(10) | Si-Ti(10) | Si-V(10) | Si-W(10) | Si-Y(10) |
| Si-Zr(10) | Ta-Ti(10) | Ta-V(10) | Ta-W(10) | Ta-Y(10) | Ta-Zr(10) | Ti-V(10) |
| Ti-W(10) | Ti-Y(10) | Ti-Zr(10) | V-W(10) | V-Y(10) | V-Zr(10) | W-Y(10) |
| W-Zr(10) | Y-Zr(10) |
Ternary Systems (204)
| Al-B-Cr(10) | Al-B-Mo(10) | Al-B-Nb(10) | Al-B-Si(10) | Al-B-Ti(10) | Al-B-V(10) |
| Al-B-Zr(10) | Al-Co-Cr(10) | Al-Co-Cu(10) | Al-Co-Fe(10) | Al-Co-Hf(8) | Al-Co-Mn(10) |
| Al-Co-Mo(10) | Al-Co-Nb(10) | Al-Co-Ni(10) | Al-Co-Si(10) | Al-Co-Ti(10) | Al-Co-V(10) |
| Al-Co-W(10) | Al-Co-Zr(10) | Al-Cr-Mo(10) | Al-Cr-Nb(10) | Al-Cr-Ni(10) | Al-Cr-Si(10) |
| Al-Cr-Ti(10) | Al-Fe-Ni(10) | Al-Hf-Nb(5) | Al-Hf-Si(10) | Al-Hf-Ti(10) | Al-Mo-Nb(10) |
| Al-Mo-Ni(10) | Al-Mo-Si(10) | Al-Mo-Ti(10) | Al-Mo-V(10) | Al-Mo-Zr(10) | Al-N-Ti(10) |
| Al-Nb-Ni(10) | Al-Nb-Si(10) | Al-Nb-Ta(10) | Al-Nb-Ti(10) | Al-Nb-V(10) | Al-Nb-Zr(10) |
| Al-Ni-Ti(10) | Al-Si-Ta(10) | Al-Si-Ti(10) | Al-Si-V(10) | Al-Si-Zr(10) | Al-Ta-Ti(10) |
| Al-Ta-V(10) | Al-Ta-Zr(10) | Al-Ti-V(10) | Al-Ti-Zr(10) | Al-V-Zr(10) | B-Cr-Nb(10) |
| B-Cr-Si(8) | B-Cr-Ta(10) | B-Cr-V(10) | B-Hf-Mo(10) | B-Hf-Nb(10) | B-Hf-Si(10) |
| B-Hf-Ti(10) | B-Hf-Zr(10) | B-Mo-Nb(10) | B-Mo-Si(10) | B-Mo-Ti(10) | B-Mo-V(10) |
| B-Mo-Zr(10) | B-Nb-Si(10) | B-Nb-Ta(10) | B-Nb-Ti(10) | B-Nb-V(10) | B-Nb-Zr(10) |
| B-Si-Ti(10) | B-Si-V(10) | B-Si-Zr(10) | B-Ta-Ti(10) | B-Ta-V(10) | B-Ti-V(10) |
| B-Ti-Zr(10) | B-V-Zr(10) | C-N-Nb(10) | Co-Cr-Cu(10) | Co-Cr-Fe(10) | Co-Cr-Hf(10) |
| Co-Cr-Mn(10) | Co-Cr-Mo(10) | Co-Cr-Nb(10) | Co-Cr-Ni(10) | Co-Cr-Si(10) | Co-Cr-Ta(10) |
| Co-Cr-Ti(10) | Co-Cr-V(10) | Co-Cr-W(10) | Co-Cr-Zr(10) | Co-Cu-Fe(10) | Co-Cu-Hf(5) |
| Co-Cu-Mn(10) | Co-Cu-Mo(5) | Co-Cu-Ni(10) | Co-Cu-Si(10) | Co-Cu-Ta(10) | Co-Cu-Ti(10) |
| Co-Cu-V(10) | Co-Cu-W(10) | Co-Cu-Zr(5) | Co-Fe-Hf(5) | Co-Fe-Mn(10) | Co-Fe-Nb(10) |
| Co-Fe-Ni(10) | Co-Fe-Si(10) | Co-Fe-Ta(10) | Co-Fe-Ti(10) | Co-Fe-V(10) | Co-Fe-W(10) |
| Co-Fe-Zr(10) | Co-Hf-Mn(5) | Co-Hf-Nb(5) | Co-Hf-Ni(5) | Co-Hf-Si(5) | Co-Hf-Ta(5) |
| Co-Hf-Ti(5) | Co-Hf-V(5) | Co-Hf-W(5) | Co-Hf-Zr(10) | Cr-Fe-Ni(10) | Cr-Hf-N(8) |
| Cr-Mo-N(8) | Cr-Mo-Nb(10) | Cr-Mo-Ni(10) | Cr-Mo-Ta(10) | Cr-Mo-Ti(10) | Cr-N-Ni(8) |
| Cr-N-V(10) | Cr-N-W(10) | Cr-N-Zr(8) | Cr-Nb-Ni(10) | Cr-Nb-Si(10) | Cr-Nb-Ta(10) |
| Cr-Nb-Ti(10) | Cr-Nb-V(10) | Cr-Ni-Ti(10) | Cr-Si-Ti(10) | Cr-Ta-Ti(10) | Cr-Ta-V(10) |
| Cr-Ti-V(10) | Fe-Mo-Nb(10) | Fe-Mo-Ni(10) | Fe-N-Nb(8) | Fe-Nb-Ni(10) | Fe-Nb-Ta(10) |
| Fe-Ni-Ti(10) | Hf-Mo-Nb(10) | Hf-Mo-Si(10) | Hf-Mo-V(10) | Hf-N-Nb(8) | Hf-N-W(6) |
| Hf-Nb-Si(10) | Hf-Nb-V(10) | Hf-Nb-Zr(5) | Hf-Si-Ti(10) | Hf-Ti-Zr(10) | Mo-N-Nb(8) |
| Mo-N-Ta(8) | Mo-Nb-Ni(10) | Mo-Nb-Si(10) | Mo-Nb-Ta(10) | Mo-Nb-Ti(10) | Mo-Nb-V(10) |
| Mo-Nb-Zr(10) | Mo-Ni-Ti(10) | Mo-Si-Ti(10) | Mo-Si-V(10) | Mo-Si-Zr(10) | Mo-Ti-V(10) |
| Mo-Ti-Zr(10) | Mo-V-Zr(10) | N-Nb-Ta(10) | N-Nb-Ti(10) | N-Nb-W(10) | N-Nb-Zr(8) |
| N-Si-Ti(8) | N-Si-V(8) | N-Si-Zr(8) | N-Ta-Ti(8) | N-Ti-V(8) | N-V-Zr(8) |
| Nb-Ni-Ti(10) | Nb-Si-Ti(10) | Nb-Si-V(10) | Nb-Si-Zr(10) | Nb-Ta-Ti(10) | Nb-Ta-V(10) |
| Nb-Ta-Zr(10) | Nb-Ti-V(10) | Nb-Ti-Zr(10) | Nb-V-Zr(10) | Si-Ta-Ti(10) | Si-Ta-V(10) |
| Si-Ta-W(10) | Si-Ti-V(10) | Si-Ti-Zr(10) | Ta-Ti-V(10) | Ta-Ti-Zr(10) | Ti-V-Zr(10) |
Database Validation and Application
The PanRHEA database is the first commercial database for alloy design and processing optimization of refractory high entropy alloys (RHEA). It has been validated by a large amount of experimental data.
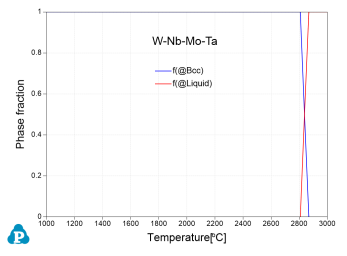
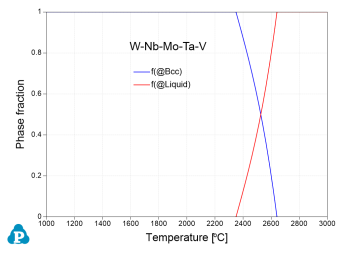
Senkov et al. [2010Sen] investigated two RHEAs W-Nb-Mo-Ta and W-Nb-Mo-Ta-V at the equiatomic ratio. Experimental characterizations of both alloys show single-Bcc microstructure. Figure 1 shows the calculated phase stability of these two alloys using the current PanRHEA database.
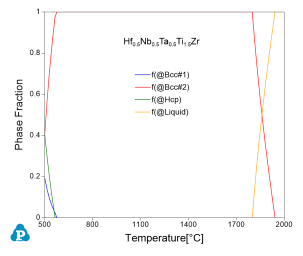
Yao et al. [2018Yao] evaluated the phase stablity of a Hf0.5Nb0.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr RHEA after annealing for two weeks at 500-900 °C. Microstructural analyses show that the RHEA is a single-phase solid solution after recrystallization at 1000 °C for 3 hours and remains in this state after a subsequent anneal at 900 °C for two weeks. However, it is unstable and forms other intermetallic phases at lower temperatures. After the anneal at 500 °C, the RHEA decomposes into multi-phase microstructures: Ti-rich Hcp phase, Bcc#1 enriches of Hf and Zr, and Bcc#2 enriches of Nb and Ta. Figure 2 shows the calculated phase equilibrium of the Hf0.5Nb0.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr vs. temperature using the PanRHEA database. Single Bcc phase is stable within a large temperature range and three phases (Bcc#1+Bcc#2+Hcp) coexist at 500 °C, which is consistent with the experimental observations well.
[2010Sen] O.N. Senkov et al., Refractory high-entropy alloys, Intermetallics, (2010), 18(9): 1758-1765
[2018Yao] J.Q. Yao et al., Phase stability of a ductile single-phase BCC Hf0.5Nb0.5Ta0.5Ti1.5Zr refractory high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics, (2018), 98: 79–88